练习 1 使用 Round-Robin 调度算法
// The introduction of scheduling classes is borrrowed from Linux, and makes the
// core scheduler quite extensible. These classes (the scheduler modules) encapsulate
// the scheduling policies.
struct sched_class {
// the name of sched_class
const char *name;
// Init the run queue
void (*init)(struct run_queue *rq);
// put the proc into runqueue, and this function must be called with rq_lock
void (*enqueue)(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc);
// get the proc out runqueue, and this function must be called with rq_lock
void (*dequeue)(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc);
// choose the next runnable task
struct proc_struct *(*pick_next)(struct run_queue *rq);
// dealer of the time-tick
void (*proc_tick)(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc);
/* for SMP support in the future
* load_balance
* void (*load_balance)(struct rq* rq);
* get some proc from this rq, used in load_balance,
* return value is the num of gotten proc
* int (*get_proc)(struct rq* rq, struct proc* procs_moved[]);
*/
};init函数指针用于初始化调度器。enqueue函数指针用于将一个进程放入调度队列中。dequeue函数指针用于将一个进程从调度队列中出队。pick_next函数指针用于从调度队列中根据算法选出下一个要被运行的进程。proc_tick函数指针用于系统时钟中断时通知调度器。
在 ucore 中,首先在 kern_init 进行内核初始化的时候调用 sched_init 进行调度器的初始化,在 Round Robin 算法中,则是将运行队列初始化,并将进程数置为 0:
static void
RR_init(struct run_queue *rq) {
list_init(&(rq->run_list));
rq->proc_num = 0;
}在 schedule 函数中,会检查当前进程是否可以继续运行,如果可以的话就重新放入队列中。然后调用 sched_class_pick_next 获取下一个执行的进程,然后将其出队,如果没有正在排队的进程,则运行 idle 进程。
void
schedule(void) {
bool intr_flag;
struct proc_struct *next;
local_intr_save(intr_flag);
{
current->need_resched = 0;
if (current->state == PROC_RUNNABLE) {
sched_class_enqueue(current);
}
if ((next = sched_class_pick_next()) != NULL) {
sched_class_dequeue(next);
}
if (next == NULL) {
next = idleproc;
}
next->runs ++;
if (next != current) {
proc_run(next);
}
}
local_intr_restore(intr_flag);
}而在 Round Robin 算法,每个进程都有固定的时间片可以执行,而且按照先来先到的顺序执行:
static void
RR_enqueue(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc) {
assert(list_empty(&(proc->run_link)));
list_add_before(&(rq->run_list), &(proc->run_link));
if (proc->time_slice == 0 || proc->time_slice > rq->max_time_slice) {
proc->time_slice = rq->max_time_slice;
}
proc->rq = rq;
rq->proc_num ++;
}
static void
RR_dequeue(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc) {
assert(!list_empty(&(proc->run_link)) && proc->rq == rq);
list_del_init(&(proc->run_link));
rq->proc_num --;
}
static struct proc_struct *
RR_pick_next(struct run_queue *rq) {
list_entry_t *le = list_next(&(rq->run_list));
if (le != &(rq->run_list)) {
return le2proc(le, run_link);
}
return NULL;
}RR_pick_next 则是简单地取出队头。
在时钟中断发生的时候,会将进程的时间减 1,如果时间片用完了,则将进程的 need_reschedule 位置 1,以便下次唤醒调度器的时候将进程调度走。
static void
RR_proc_tick(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc) {
if (proc->time_slice > 0) {
proc->time_slice --;
}
if (proc->time_slice == 0) {
proc->need_resched = 1;
}
}练习 2 实现 Stride Scheduling 调度算法
在 Stride Scheduling 中,使用了斜堆加速调度。
static inline void
skew_heap_init(skew_heap_entry_t *a)
{
a->left = a->right = a->parent = NULL;
}
static inline skew_heap_entry_t *
skew_heap_merge(skew_heap_entry_t *a, skew_heap_entry_t *b,
compare_f comp)
{
if (a == NULL) return b;
else if (b == NULL) return a;
skew_heap_entry_t *l, *r;
if (comp(a, b) == -1)
{
r = a->left;
l = skew_heap_merge(a->right, b, comp);
a->left = l;
a->right = r;
if (l) l->parent = a;
return a;
}
else
{
r = b->left;
l = skew_heap_merge(a, b->right, comp);
b->left = l;
b->right = r;
if (l) l->parent = b;
return b;
}
}
static inline skew_heap_entry_t *
skew_heap_insert(skew_heap_entry_t *a, skew_heap_entry_t *b,
compare_f comp)
{
skew_heap_init(b);
return skew_heap_merge(a, b, comp);
}
static inline skew_heap_entry_t *
skew_heap_remove(skew_heap_entry_t *a, skew_heap_entry_t *b,
compare_f comp)
{
skew_heap_entry_t *p = b->parent;
skew_heap_entry_t *rep = skew_heap_merge(b->left, b->right, comp);
if (rep) rep->parent = p;
if (p)
{
if (p->left == b)
p->left = rep;
else p->right = rep;
return a;
}
else return rep;
}
斜堆是一种特殊的二叉树,特点是合并的时候比普通的堆更快。
为此,首先定义了一个比较两个进程的步长的函数:
#define BIG_STRIDE (1 << 30) /* you should give a value, and is ??? */
/* The compare function for two skew_heap_node_t's and the
* corresponding procs*/
static int
proc_stride_comp_f(void *a, void *b)
{
struct proc_struct *p = le2proc(a, lab6_run_pool);
struct proc_struct *q = le2proc(b, lab6_run_pool);
int32_t c = p->lab6_stride - q->lab6_stride;
if (c > 0) return 1;
else if (c == 0) return 0;
else return -1;
}初始化的时候,则使用 lab6_run_pool 变量,初始为 NULL 指针。
/*
* stride_init initializes the run-queue rq with correct assignment for
* member variables, including:
*
* - run_list: should be a empty list after initialization.
* - lab6_run_pool: NULL
* - proc_num: 0
* - max_time_slice: no need here, the variable would be assigned by the caller.
*
* hint: see libs/list.h for routines of the list structures.
*/
static void
stride_init(struct run_queue *rq) {
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE
* (1) init the ready process list: rq->run_list
* (2) init the run pool: rq->lab6_run_pool
* (3) set number of process: rq->proc_num to 0
*/
rq->lab6_run_pool = NULL;
rq->proc_num = 0;
}入队的函数则如下,使用 skew_heap_insert 将进程按步长作比较插入到斜堆中,然后重新分配时间片,最后 proc_num++。
/*
* stride_enqueue inserts the process ``proc'' into the run-queue
* ``rq''. The procedure should verify/initialize the relevant members
* of ``proc'', and then put the ``lab6_run_pool'' node into the
* queue(since we use priority queue here). The procedure should also
* update the meta date in ``rq'' structure.
*
* proc->time_slice denotes the time slices allocation for the
* process, which should set to rq->max_time_slice.
*
* hint: see libs/skew_heap.h for routines of the priority
* queue structures.
*/
static void
stride_enqueue(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc) {
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE
* (1) insert the proc into rq correctly
* NOTICE: you can use skew_heap or list. Important functions
* skew_heap_insert: insert a entry into skew_heap
* list_add_before: insert a entry into the last of list
* (2) recalculate proc->time_slice
* (3) set proc->rq pointer to rq
* (4) increase rq->proc_num
*/
rq->lab6_run_pool = skew_heap_insert(rq->lab6_run_pool, &proc->lab6_run_pool, proc_stride_comp_f);
if (proc->time_slice == 0 || proc->time_slice > rq->max_time_slice) {
proc->time_slice = rq->max_time_slice;
}
proc->rq = rq;
++rq->proc_num;
}出队的函数则和入队相反:
/*
* stride_dequeue removes the process ``proc'' from the run-queue
* ``rq'', the operation would be finished by the skew_heap_remove
* operations. Remember to update the ``rq'' structure.
*
* hint: see libs/skew_heap.h for routines of the priority
* queue structures.
*/
static void
stride_dequeue(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc) {
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE
* (1) remove the proc from rq correctly
* NOTICE: you can use skew_heap or list. Important functions
* skew_heap_remove: remove a entry from skew_heap
* list_del_init: remove a entry from the list
*/
rq->lab6_run_pool = skew_heap_remove(rq->lab6_run_pool, &proc->lab6_run_pool, proc_stride_comp_f);
// list_del_init(&proc->run_link);
// proc->rq = NULL;
rq->proc_num--;
}在 pick_next 中,直接取斜堆堆顶元素就是需要运行的进程,同时需要更新进程的 stride 值,更新之后需要重新插入到堆中:
/*
* stride_pick_next pick the element from the ``run-queue'', with the
* minimum value of stride, and returns the corresponding process
* pointer. The process pointer would be calculated by macro le2proc,
* see kern/process/proc.h for definition. Return NULL if
* there is no process in the queue.
*
* When one proc structure is selected, remember to update the stride
* property of the proc. (stride += BIG_STRIDE / priority)
*
* hint: see libs/skew_heap.h for routines of the priority
* queue structures.
*/
static struct proc_struct *
stride_pick_next(struct run_queue *rq) {
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE
* (1) get a proc_struct pointer p with the minimum value of stride
(1.1) If using skew_heap, we can use le2proc get the p from rq->lab6_run_pool
(1.2) If using list, we have to search list to find the p with minimum stride value
* (2) update p;s stride value: p->lab6_stride
* (3) return p
*/
if (rq->proc_num == 0) return NULL;
struct proc_struct* proc = le2proc(rq->lab6_run_pool, lab6_run_pool);
rq->lab6_run_pool = skew_heap_remove(rq->lab6_run_pool, &proc->lab6_run_pool, proc_stride_comp_f);
proc->lab6_stride += BIG_STRIDE / (proc->lab6_priority == 0 ? 1 : proc->lab6_priority);
rq->lab6_run_pool = skew_heap_insert(rq->lab6_run_pool, &proc->lab6_run_pool, proc_stride_comp_f);
return proc;
}时钟中断函数和 Round Robin 算法一样:
/*
* stride_proc_tick works with the tick event of current process. You
* should check whether the time slices for current process is
* exhausted and update the proc struct ``proc''. proc->time_slice
* denotes the time slices left for current
* process. proc->need_resched is the flag variable for process
* switching.
*/
static void
stride_proc_tick(struct run_queue *rq, struct proc_struct *proc) {
/* LAB6: YOUR CODE */
if (proc->time_slice > 0) {
proc->time_slice --;
}
if (proc->time_slice == 0) {
proc->need_resched = 1;
}
}运行结果:
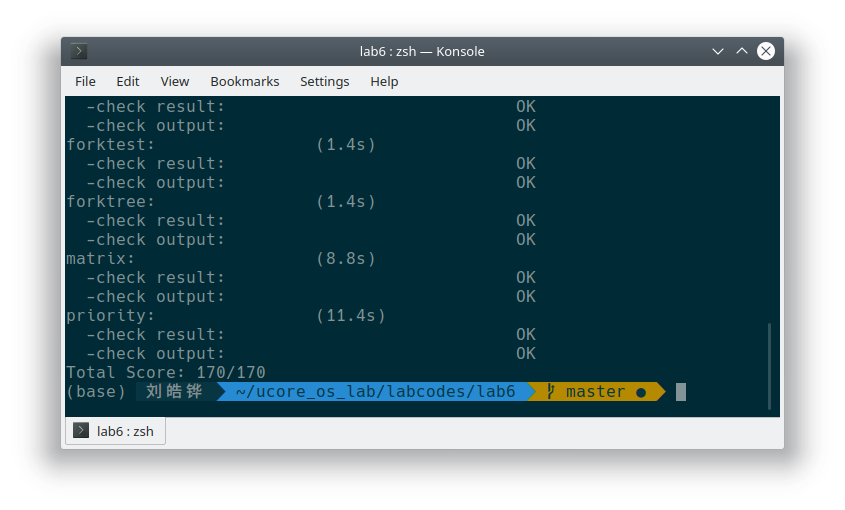
练习 3 阅读分析源代码
结合中断处理和调度程序,再次理解进程控制块中的 trapframe 和 context 在进程切换时作用。
__alltraps:
# push registers to build a trap frame
# therefore make the stack look like a struct trapframe
pushl %ds
pushl %es
pushl %fs
pushl %gs
pushal
# load GD_KDATA into %ds and %es to set up data segments for kernel
movl $GD_KDATA, %eax
movw %ax, %ds
movw %ax, %es
# push %esp to pass a pointer to the trapframe as an argument to trap()
pushl %esp
# call trap(tf), where tf=%esp
call trap
# pop the pushed stack pointer
popl %esp
__trapret:
# restore registers from stack
popal
# restore %ds, %es, %fs and %gs
popl %gs
popl %fs
popl %es
popl %ds
# get rid of the trap number and error code
addl $0x8, %esp
irettrapframe 用于在中断发生的时候保存进程的现场,如果发生特权级转换还会保存段寄存器等信息,在 __alltrpas 中保存,__trapret 中恢复。
switch_to: # switch_to(from, to)
# save from's registers
movl 4(%esp), %eax # eax points to from
popl 0(%eax) # save eip !popl
movl %esp, 4(%eax)
movl %ebx, 8(%eax)
movl %ecx, 12(%eax)
movl %edx, 16(%eax)
movl %esi, 20(%eax)
movl %edi, 24(%eax)
movl %ebp, 28(%eax)
# restore to's registers
movl 4(%esp), %eax # not 8(%esp): popped return address already
# eax now points to to
movl 28(%eax), %ebp
movl 24(%eax), %edi
movl 20(%eax), %esi
movl 16(%eax), %edx
movl 12(%eax), %ecx
movl 8(%eax), %ebx
movl 4(%eax), %esp
pushl 0(%eax) # push eip
ret
而 context 只是用于进程调度 schedule 的时候切换进程的时候保存和恢复上下文使用的,在 switch_to 函数中保存和恢复。